Case study
Transforming fracture detection accuracy at Kettering General Hospital
Share this case study
About Kettering General Hospital
Using RBfracture™ in an NHS setting
Kettering General Hospital (KGH) partnered with Radiobotics to assess the impact of RBfracture in improving fracture detection in a high-demand NHS setting.
The aim was to reduce missed fractures in the KHG’s Accident and Emergency department (A&E), especially during off hours where acute musculoskeletal exams are not immediately reported by radiologists or reporting radiographers.


Can an AI-powered solution like RBfracture™ that automatically detects trauma-related findings reduce the number of missed fractures in an NHS A&E?
Purpose, scale, and timeline
Audit details
The audit included an evaluation of RBfracture™ through a focused retrospective review of 319 MSK cases
The prospective analysis also assessed RBfracture’s impact on reducing missed fracture rates among Accident and Emergency department clinicians
RBfracture™ v.1.7 deployed
Go-live in A&E
Update to RBfracture™ v.1.8
Update to RBfracture™ v.2.0
Audit completion
Download the Kettering General Hospital audit
Results
We saw a reduction in missed fractures by 86% — a significant decrease in missed fractures by Emergency clinicians
94%
Accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity
15s
Median processing time per exam
86%
Reduction in missed fractures
The value in AN NHS setting
The value of RBfracture™
The AI-driven support of trauma related findings can enhance diagnostic precision, reduce missed fractures, and enable faster, more reliable fracture diagnoses, particularly in high-demand settings
Reduces missed fractures
Improves patient outcomes
clinician skills
A must-have for ED and Radiology
Ben Madden
Lead Reporting Radiographer
Kettering General Hospital Foundation Trust
Measuring the standalone performance of RBfracture™
RBfracture’s performance was assessed by calculating accuracy, sensitivity (true positive rate), and specificity (true negative rate) on a dataset of 319 cases selected by KGH.
The Kettering General Hospital audit exams
A total of 319 patient exams were included in the audit.
Consecutive radiographs from 16 random days in November ‘23 through January ‘24 were used for the audit. Two Reporting Radiographers independently reviewed the radiographs, and their consensus served as the reference standard for RBfracture. In cases of disagreement, a third reviewer was consulted.
At least one fracture was present in 78/319 (24%) of the cases. The median patient age was 52 (2, 94) years, and the Hip/Pelvis was the most frequently examined body part.
| Body part | Number | Fracture prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Finger | 11 (3%) | 27% |
| Hand | 34 (11%) | 26% |
| Wrist | 29 (9%) | 24% |
| Forearm | 10 (3%) | 40% |
| Elbow | 11 (3%) | 27% |
| Humerus | 8 (3%) | 38% |
| Shoulder | 38 (12%) | 39% |
| Clavicle | 3 (1%) | 33% |
| Toe | 3 (1%) | 0% |
| Foot | 26 (8%) | 35% |
| Ankle | 32 (10%) | 16% |
| Tibia/Fibula | 8 (3%) | 25% |
| Knee | 43 (13%) | 12% |
| Femur | 6 (2%) | 17% |
| Hip/Pelvis | 57 (18%) | 19% |
Confusion matrix with derived performance measures
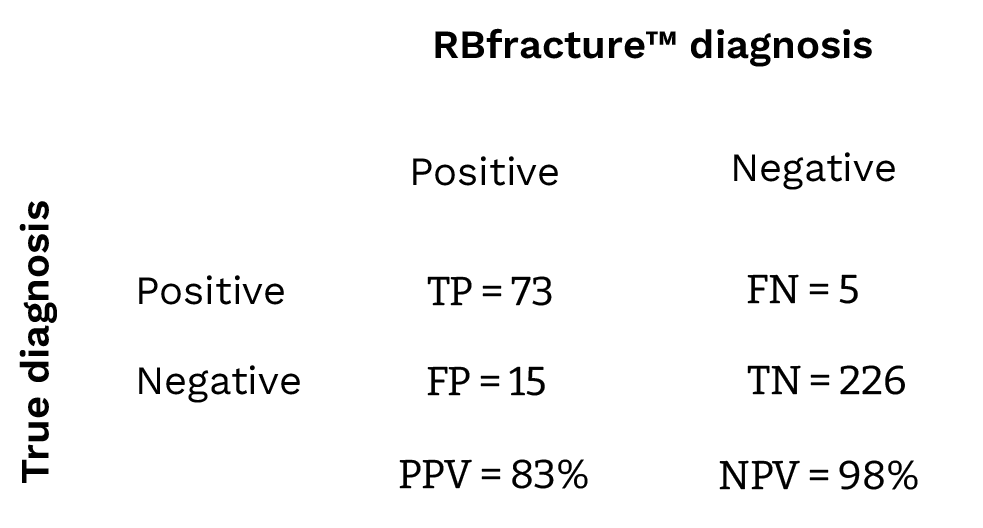
True-Positive (TP), True-Negative (TN), False-Positive (FP), False-Negative (FN), Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative Predictive Value (NPV)
