Case study
Lipohemarthrosis detection in X-ray images with RBfracture™
Share this case study
Lipohemarthrosis and its significance
What is Lipohemarthrosis?
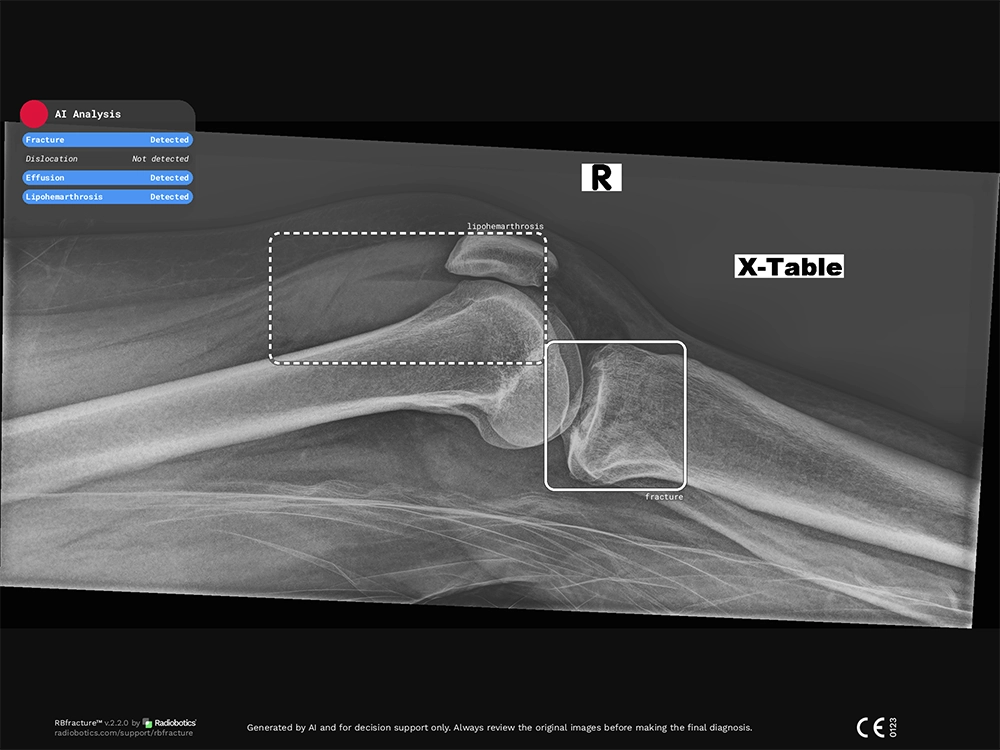
Lipohemarthrosis is a condition that occurs when both fat and blood enter a joint cavity following a bone fracture, typically resulting from intra-articular fractures (fractures that extend into a joint). When this happens, the fatty bone marrow leaks into the joint through the fractured bone layer that normally encompasses the bone marrow.
The mix of fat and blood will separate in distinct layers, similarly to how oil separates from water when mixed in the same container. This layering effect of fat and blood within the joint is a reliable indicator of a fracture following a recent trauma.
An indicator for occult knee fractures
Recognizing lipohemarthrosis is crucial in trauma settings, as its presence on imaging strongly suggests occult knee fractures.
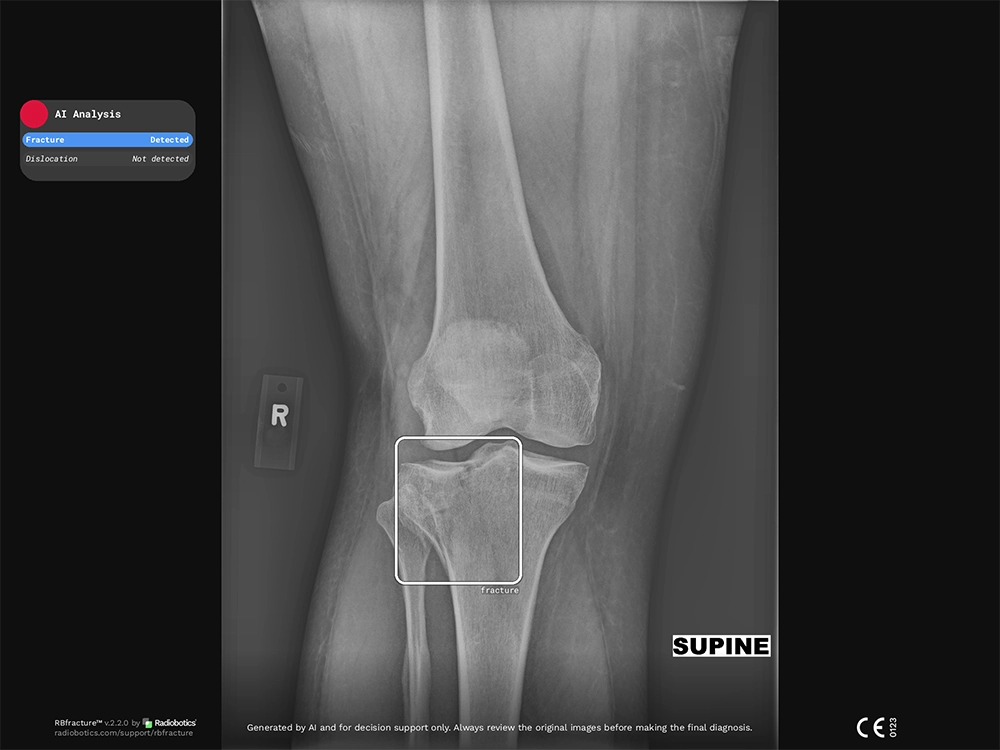
Occult fractures, such as subtle tibial plateau fractures, can be easily missed if only gross structural damage is sought.
In busy emergency settings, such subtle indicators can be easily overlooked, potentially leading to missed or delayed diagnoses of serious fractures.
Detecting lipohemarthrosis
Audit details
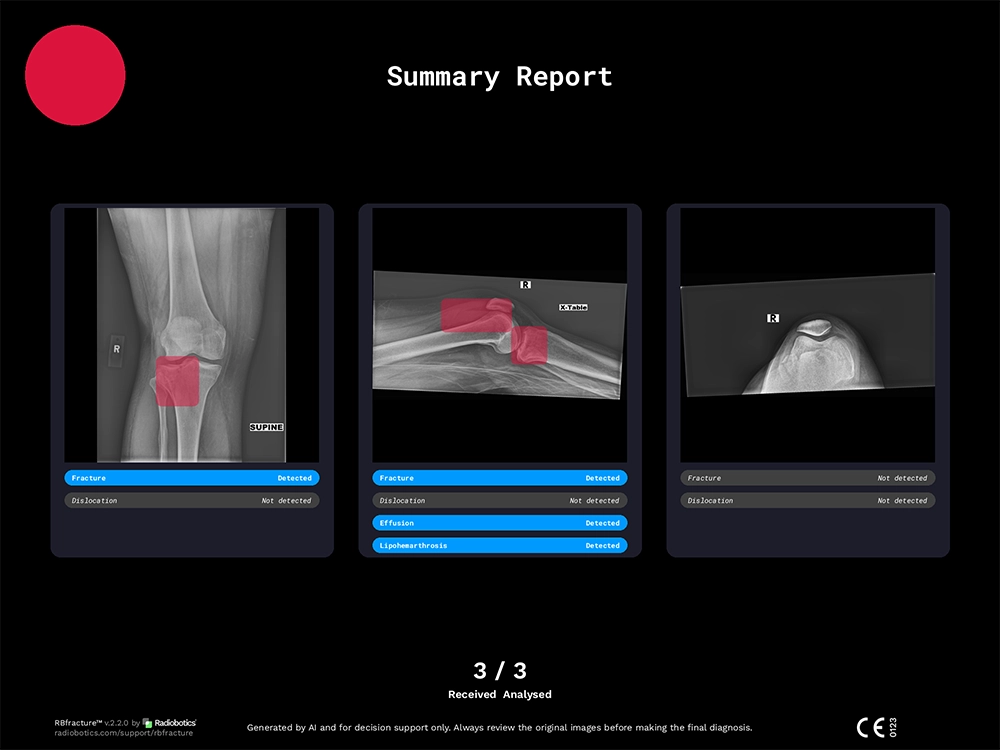
We conducted an internal audit of RBfracture to detect lipohemarthrosis on an unseen test dataset of 373 knee cases
Radiographs were independently annotated by two qualified annotators who, supported by the original radiological report, analysed the radiographs and identified fractures in the images. In case of disagreement between the two annotators, adjudication was conducted by a third independent annotator who chose which annotator was right, supported by the original radiological report. In case of disagreement among all three annotators, the study was discarded.
Results
This case illustrates how RBfracture’s precise detection can play a pivotal role in managing trauma cases effectively, particularly in high-demand, high-impact environments like emergency departments
93%
Sensitivity
98%
Specificity
99%
AUC
Why early and accurate detection matters
Intra-articular fractures are particularly prone to complications, including joint instability, long-term pain, and arthritis if left untreated. Detecting associated signs like lipohemarthrosis allows healthcare providers to treat these fractures promptly, improving patient outcomes and potentially reducing the need for complex, long-term interventions.